BeoLiving Intelligence (BLI) provides robust support for IP cameras. However, the integration process can be complex due to the unique configuration required for each camera provider. This guide will help you understand the requirements and steps for integrating IP cameras with BLI.
Camera Compatibility Criteria
For a camera to be compatible with BLI, it must meet the following criteria:
- Authentication: If the camera requires authentication, it should support either Digest or HTTP Basic authentication.
- Protocols: The camera should support at least one of the following protocols:
- Snapshot image: A camera snapshot is available on an HTTP URL. This URL can be used directly in a browser, which means that BLI can process it.
- MJPEG HTTP stream: A JPEG snapshot stream is available on an HTTP URL.
- RTSP stream with H264 codec: The camera provides an RTSP or SRTSP stream URL and the video is encoded in H264. While other codecs are supported on the apps, H264 is required for full support across all BLI interfaces.
Any camera that meets these requirements should be compatible with BLI.
Client Stream Priority
BLI clients will utilize the most optimal stream in each scenario. The table below illustrates the priority each client assigns to each type of stream (where 1 is the top choice):
| Client | RTSP | MJPEG stream | Snapshot image |
|---|---|---|---|
| BeoLiving App | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Web client | 1 (*) | 2 | 3 |
| Home Control panel on B&O TV | 1 (*) | 2 | 3 |
| Home Control on legacy B&O TV | None | 1 | 2 |
(*) Only supported since BLI Generation 3 and requires that the camera streams use the H264 codec. In older BLIs, the streams will not be visible.
Camera Configuration
Cameras can be configured in two ways: as ONVIF cameras or Generic HTTP cameras.
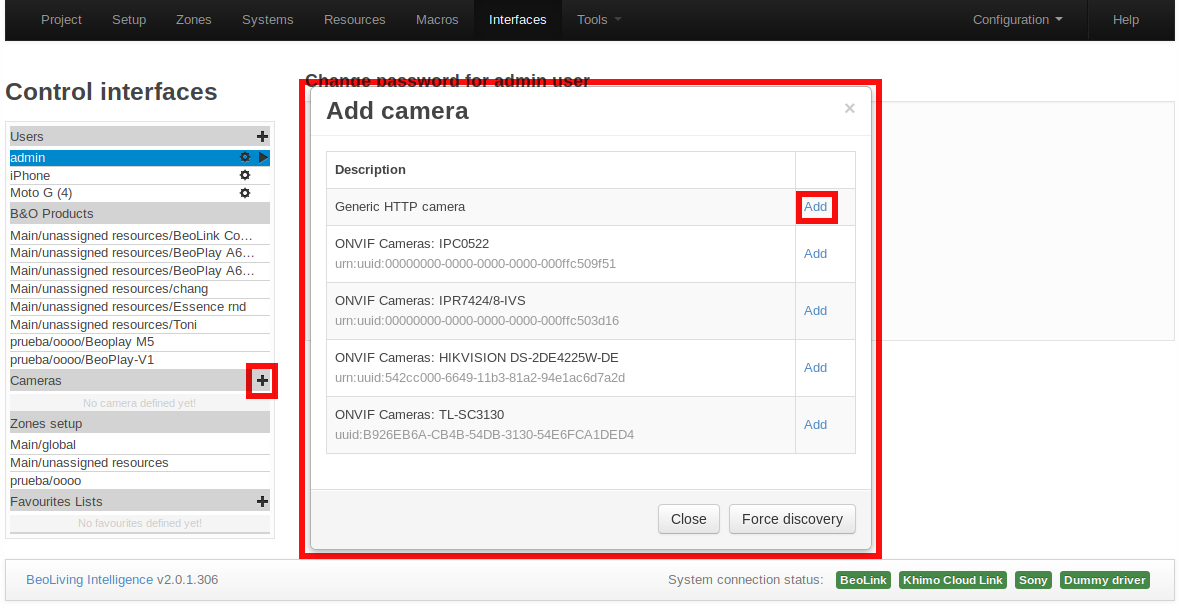
ONVIF Camera Configuration
ONVIF cameras should be automatically detected by BLI. In the Admin panel, under the Interfaces section, pressing the [+] button will display a table with all discovered cameras.
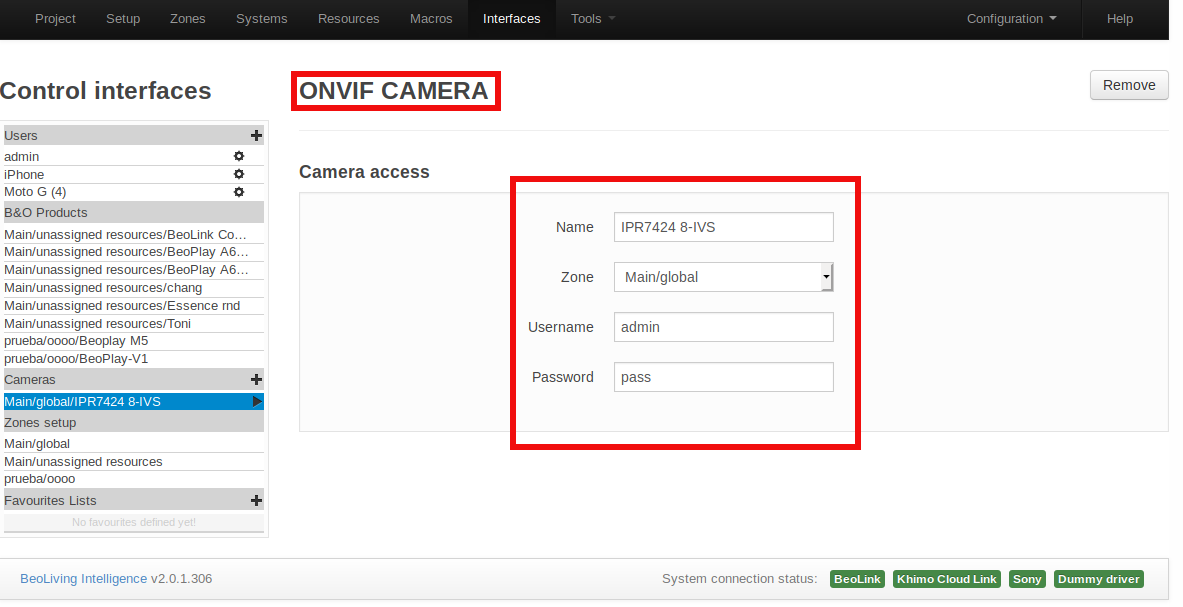
If a camera is not displayed and has not been previously added, please refer to the camera manual and settings to enable ONVIF on the camera. Often, even if cameras state they support ONVIF, it is disabled by default and must be manually enabled in the CCTV camera settings.
BLI automatically discovers and presents ONVIF compliant cameras. Only the username and password may be needed. However, ONVIF implementation varies from camera to camera, so not all ONVIF labeled cameras are supported. Once the credentials are entered correctly, all paths and options on the camera are automatically configured.
Please be aware that there are companies improperly claiming ONVIF conformance for their products, compatibility can be verified on www.onvif.org/conformant-products/. You must also take into account that some ONVIF compatible cameras don’t have the functionality enabled by default (e.g.: Hikvision https://www.hikvision.com/ueditor/net…) and must be “manually” enabled.
In the case that the camera failed to be added or it doesn’t work after added, you may need to manually add it as a Generic HTTP camera.
Generic HTTP Cameras Configuration
The Generic HTTP camera option should be used if:
- The camera is not ONVIF compliant.
- The camera uses secure RTSP (RTSPS).
- Fine-grained control of the camera configuration is needed.
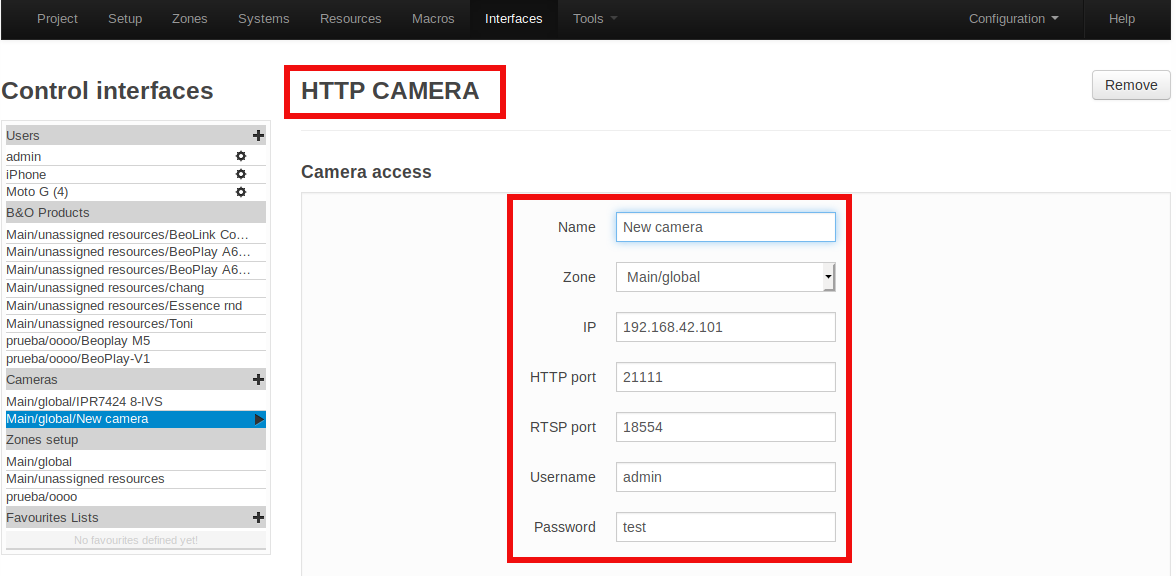
For a generic HTTP camera, both the username and password are used for basic or digest HTTP authentication.
You need to find and fill the following information from the CCTV camera provider documentation and the configuration on the camera hardware itself:
- IP: The IP address of the camera, such as
192.168.1.37. - HTTP port: The port where the camera accepts HTTP connections. This is generally
80. - RTSP port: The port where the camera accepts RTSP connections. This is generally
554. - Use secure RTSP: Set this field to TRUE if the connection to the camera should be performed via RTSPS.
- Secure fingerprint: When connecting via RTSPS, the secure fingerprint is needed to ensure the connection to the camera is secure. This field can be updated from the edition panel.
In addition to the connection options, the following paths can be configured:
- RTSP HD stream: The path to the main RTSP stream, if supported.
- RTSP substream: The path to the RTSP substream, if supported.
- High-resolution image: The path for getting a high-resolution image.
- Low-resolution image: The path for getting a low-resolution image.
- High-resolution MJPEG: The path for getting a high-resolution MJPEG.
- Low-resolution MJPEG: The path for getting a low-resolution MJPEG.
Other optional commands can be provided for cameras with pan/tilt/zoom control.
Required Paths and Camera Configuration
If the camera supports image retrieval, then at least one of the image paths should be set.
If the camera supports RTSP connections, then at least the RTSP stream path should be set. Once the RTSP paths are set, BLI will check for supported codecs on the camera.
Once the paths are configured, the Realtime preview component can be used to check if everything works as expected. The following buttons will be available:
- Image HD: If the High-resolution image is correctly configured, an HD image stream will be shown.
- Image SD: If the Low-resolution image is correctly configured, an SD image stream will be shown.
- RTSP HD: If the RTSP stream is correctly configured and the codecs are supported, an HD video stream will be shown.
- RTSP SD: If the RTSP substream is correctly configured and the codecs are supported, an SD video stream will be shown.
Raw Edit Option
Entering all these path fields into edit-boxes can be time-consuming. By pressing the Raw edit button, a text representation of all the fields is provided. This can be copied/pasted or edited in a preferred text editor. More importantly, the text can be copied and pasted when setting up other similar cameras.
Examples: From URL to camera settings
If a snapshot of a camera could be accessed at http://cctv:pass@192.168.1.33/snapshot then the camera configuration into the BLI should be:
- IP:
192.168.1.33 - Username:
cctv - Password:
pass - HTTP port:
80 - High-resolution image:
/snapshot
If a rtsp of the camera is accessible at rtsp://admin:pa55@192.168.1.34:554/highResCamera and it is possible to connect using a thirdparty client (Like VLC), then the camera settings should be:
- IP:
192.168.1.34 - Username:
admin - Password:
pa55 - RTSP port:
554 - RTSP HD stream:
/highResCamera
Troubleshooting
RTSP camera connection is too slow
The video is encoded in two different frames: the I-Frames and the P-Frames. The I-Frame (also known as key frame or IDR-Frames) contains a full copy of the image, and the P-Frames are differences from the last image. To display an image, a client must wait until the first I-Frame is received. The I-Frame generation time is governed by the CCTV camera. Some cameras may have a large interval between I-Frames, making the connection very slow and also hurting the latency for HLS connections (used in for web browser view).
If the connection seems too slow, try changing the CCTV camera encoding settings, specifically lowering the I-Frame generation frequency. Please refer to the camera documentation to find how to change this. It may be called Key Frame Interval, I-Frame Interval or Group of Pictures (GOP).
For example, if a camera’s I-Frame interval is set to 60 frames and the FPS is set to 10, it can take up to 6 seconds to get the first video image displayed in the camera client. Also, setting the I-Frame interval too low will impact the bandwidth usage, so a good balance for the given network and camera is needed. Usually, something about 2 seconds should work fine.
RTSP Camera does not connect
Try to connect to the camera using a thirdparty client, like VLC. The full RTSP path to test with should be of the form: rtsp://$user:$password@$IP:$PORT/$rtspPath.
- If it is not working: check the network settings until you are able to connect.
-
If it is working:
- Check the BeoLiving Intelligence settings for the camera and verify that all the configuration is algined with the rtsp uri that you tested on the thirdparty tool.
- Check that the camera supports H264.
- Try to force your camera to RTSP TCP mode.
- Check the BeoLiving Intelligence logs, check any message coming from mediamtx or camera domain.
- Try to connect to the camera using the rtsp stream path provider by the BLI by opening rtsp://$GATEWAY_HOST:554/$AREA/$ZONE/CAMERA/$NAME (for example with VLC), in this way you can see if the problem is on the BLI clients (probably missing codec) or into the connection from the BLI to the camera.
- If nothing else worked, reach us out at support+cctv@khimo.com